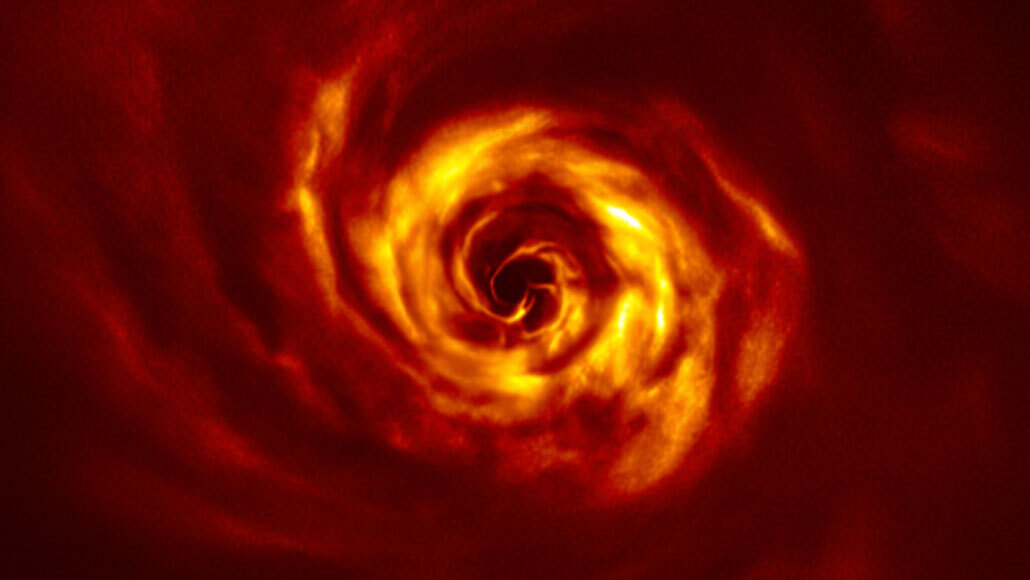
astronomy: The area of science that deals with celestial objects, space and the physical universe. People who work in this field are called astronomers.
astrophysics: An area of astronomy that deals with understanding the physical nature of stars and other objects in space. People who work in this field are known as astrophysicists.
colleague: Someone who works with another; a co-worker or team member.
constellation: Patterns formed by prominent stars that lie close to each other in the night sky. Modern astronomers divide the sky into 88 constellations, 12 of which (known as the zodiac) lie along the sun’s path through the sky over the course of a year. Cancri, the original Greek name for the constellation Cancer, is one of those 12 zodiac constellations.
cosmos: (adj. cosmic) A term that refers to the universe and everything within it.
exoplanet: Short for extrasolar planet, it’s a planet that orbits a star outside our solar system.
gas giant: A giant planet that is made mostly of the gases helium and hydrogen. Jupiter and Saturn are gas giants.
infrared: A type of electromagnetic radiation invisible to the human eye. The name incorporates a Latin term and means “below red.” Infrared light has wavelengths longer than those visible to humans. Other invisible wavelengths include X-rays, radio waves and microwaves. Infrared light tends to record the heat signature of an object or environment.
Jupiter: (in astronomy) The solar system’s largest planet, it has the shortest day length (10 hours). A gas giant, its low density indicates that this planet is composed of light elements, such as hydrogen and helium. This planet also releases more heat than it receives from the sun as gravity compresses its mass (and slowly shrinks the planet).
light-year: The distance light travels in one year, about 9.48 trillion kilometers (almost 6 trillion miles). To get some idea of this length, imagine a rope long enough to wrap around the Earth. It would be a little over 40,000 kilometers (24,900 miles) long. Lay it out straight. Now lay another 236 million more that are the same length, end-to-end, right after the first. The total distance they now span would equal one light-year.
mass: A number that shows how much an object resists speeding up and slowing down — basically a measure of how much matter that object is made from.
planet: A celestial object that orbits a star, is big enough for gravity to have squashed it into a roundish ball and has cleared other objects out of the way in its orbital neighborhood. To accomplish the third feat, the object must be big enough to have pulled neighboring objects into the planet itself or to have slung them around the planet and off into outer space.
solar system: The eight major planets and their moons in orbit around our sun, together with smaller bodies in the form of dwarf planets, asteroids, meteoroids and comets.
star: The basic building block from which galaxies are made. Stars develop when gravity compacts clouds of gas. When they become hot enough, stars will emit light and sometimes other forms of electromagnetic radiation. The sun is our closest star.
sun: The star at the center of Earth’s solar system. It is about 27,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Also a term for any sunlike star.
wave: A disturbance or variation that travels through space and matter in a regular, oscillating fashion.