Brain
-
 Brain
BrainParakeets talk using brain areas similar to ours
Brain activity during vocalizing in small parrots — called budgerigars or parakeets — shows a similar pattern to what’s seen in people.
-
 Physics
PhysicsMuch of the sun’s light is green. Why does it look yellow?
Sunlight's peak intensity is at a green wavelength. Here’s why it doesn’t appear that way to us.
-
 Brain
BrainLet’s learn about memory
Brain injuries, drug use and other factors can impair our memory. But targeted practice and healthy habits can boost our ability to remember.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentMore and more, microplastics are collecting in our brains
Over eight years, the mass of microplastics in human brains increased by some 50 percent. There are growing hints that internal microplastics may harm us.
By Laura Sanders and Janet Raloff -
 Brain
BrainBrain scans may offer clues to the mental health of trans youth
A teen researcher identified a possible link between brain development and mental health in young trans people.
-
 Brain
BrainScientists Say: Neuroplasticity
Neurons in the brain forge new connections and sometimes trim back old ones. This capacity for change allows us to learn new skills and recover from injury.
-
 Brain
BrainExplainer: How our body deals with stress
Our autonomic nervous system balances two natural responses. If stressed or overwhelmed, simple techniques can help to restore that balance.
-
 Tech
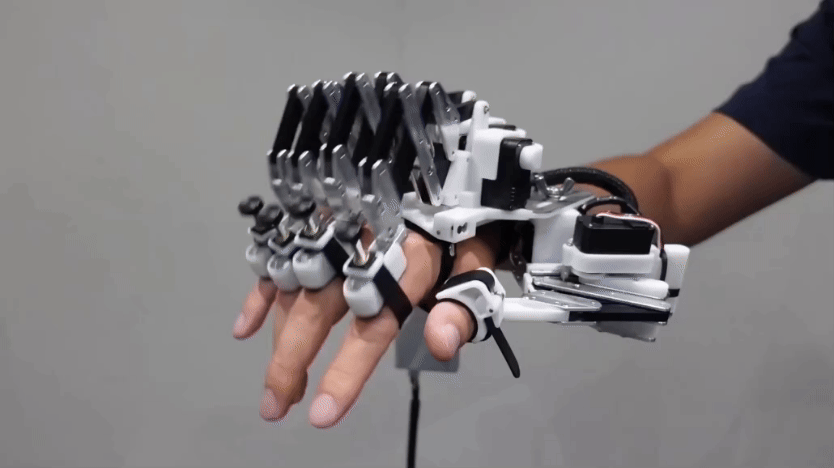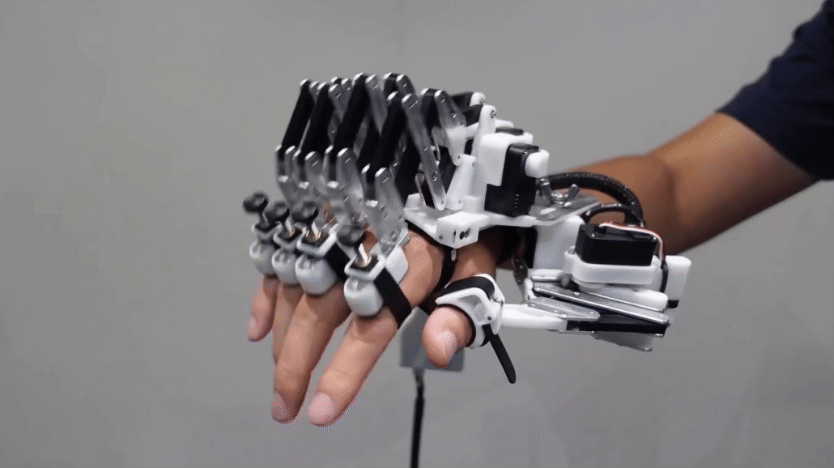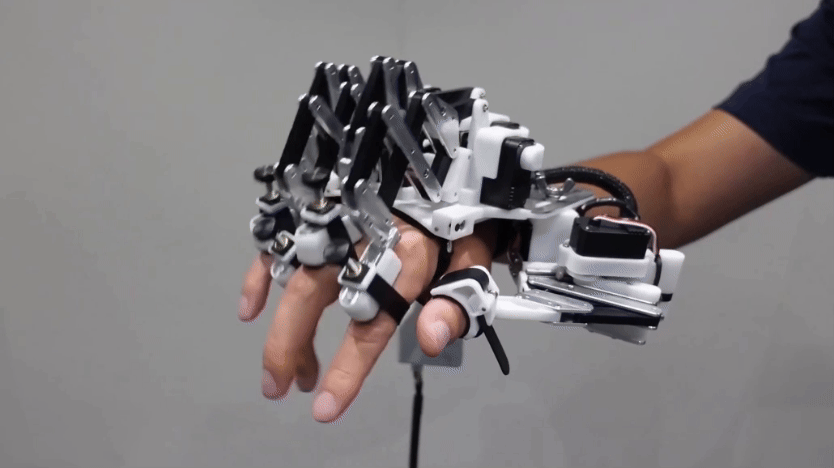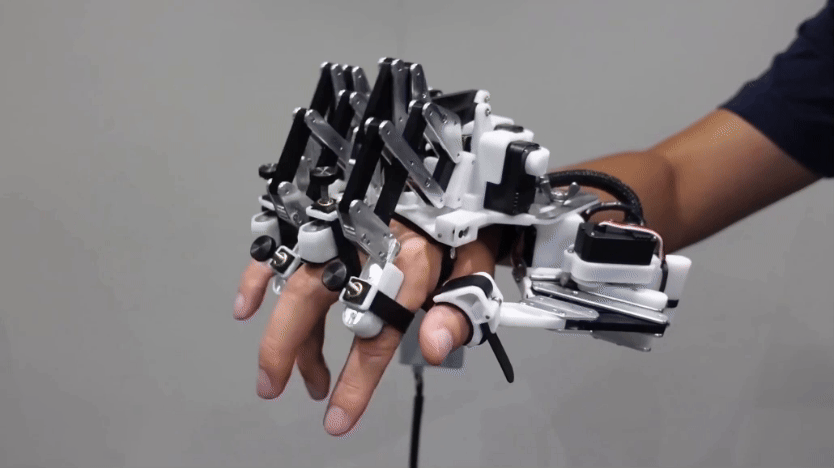
TechA robotic hand helps piano players’ fingers move faster
Robotic devices like this might someday help musicians, gamers, athletes or even surgeons improve their dexterity.
-
 Brain
BrainHaving sparse links in the hippocampus may maximize memory storage
Tissue from the memory centers of people’s brains reveal relatively few links among nerve cells in the hippocampus. But they carried strong, reliable signals.
-
 Brain
BrainCould the magic of memory manipulation ever become real?
Someday, technology might be able to help people better hold onto memories or forget bad ones.
-
 Brain
BrainScientists are exploring why some people don’t have a mind’s eye
A researcher with aphantasia is studying how different senses work together in the brain — and when they don’t.
-
 Brain
BrainPurple exists only in our brains
Most colors represent a single wavelength of light. But your brain invents purple to deal with wavelengths from opposite ends of the visible spectrum.
By Tammy Awtry