Materials Science
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryLight could make some hospital surfaces deadly to germs
A new surfacing material can disinfect itself. Room lighting turns on this germ-killing property, which could make the material attractive to hospitals.
-
 Computing
ComputingZap! Laser tattoos could create electronics to eat or wear
Lasers can tattoo a nontoxic form of carbon onto everyday items. This one day could lead to wearable — even edible — electronics.
-
 Tech
TechElectricity sensor harnesses a shark’s secret weapon
A new “quantum” material mimics the sensors that help a shark sense its prey. Like a shark, it can detect tiny electric fields.
-
 Chemistry
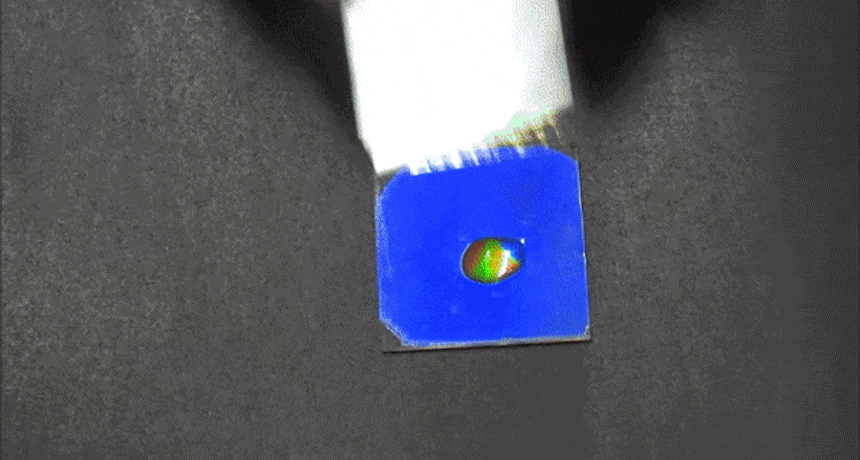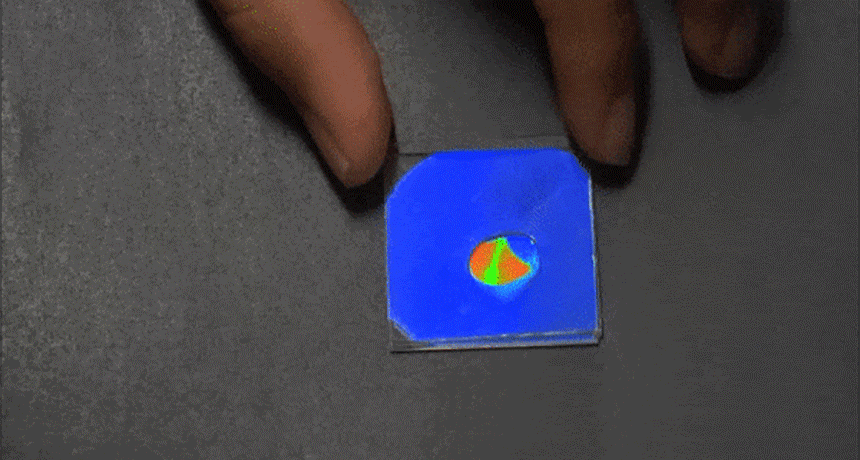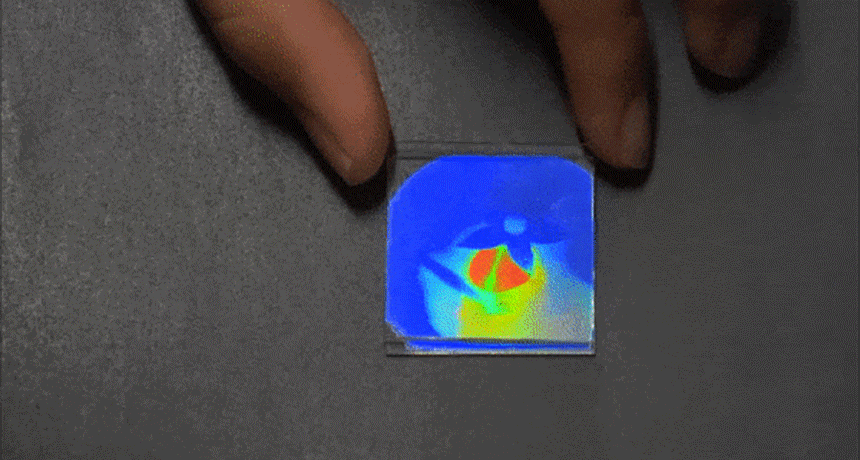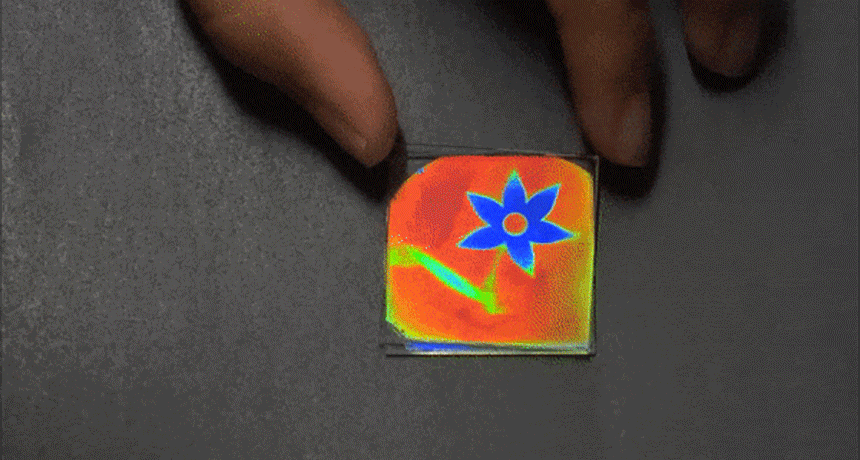
ChemistryMoisture unmasks camouflaged message
Researchers have developed a new type of chemical that will mask some hidden message — until you add water.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceNew device makes water give up its sounds
A new device can dramatically boost the ability of people above the water’s surface to hear what’s going on below.
By Dan Garisto -
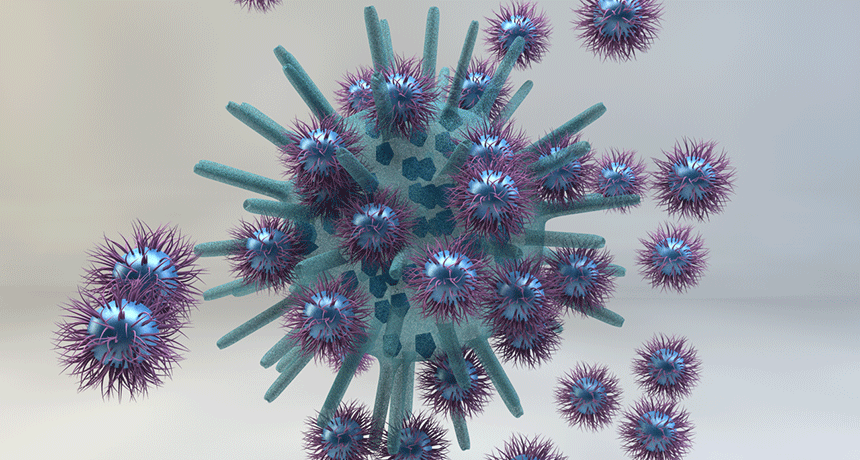 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHairy nanoparticles put viruses in a deadly embrace
Current drugs can’t stop viruses for good. But newly developed hairy nanoparticles just might. They surround and put pressure on the viruses, which ultimately destroys them.
By Ilima Loomis -
 Agriculture
AgricultureNew ‘tattoo’ could lead to drought-tolerant crops
Scientists create stick-on 'plant tattoo.' It measures how efficiently crops use water, a key to better identifying breeding stock for more drought-resistant crops.
-
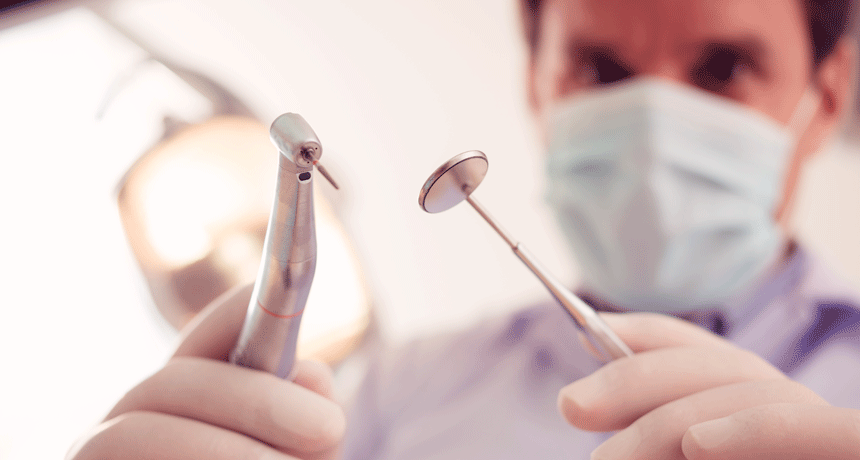 Archaeology
ArchaeologyCool Jobs: Drilling into the secrets of teeth
A bioengineer, a biologist and an archaeologist all study teeth to explore new materials, to grow better tissues and to learn more about prehistoric humans.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew treatment could calm temperature-sensitive teeth
Dentists aren’t happy with today’s treatments for sensitive teeth. Sand-like nanoparticles carrying green tea extract could bring longer pain relief.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceWant a tougher space suit? Just add liquid
Using a special liquid, engineers are designing new treatments for spacesuits so that they can better resist puncturing from tiny meteorites and other hazards.
By Marcus Woo -
 Genetics
GeneticsOne day, your sunscreen may be made from DNA
A new approach to sunscreen could use a thin layer of DNA to protect skin cells — and hopefully prevent cancer.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceYou can peel permanent marker, intact, off of glass
The surface tension of water can essentially scrape a thin film of some water-repellent material — such as permanent ink — off of glass.