Analyze This: Bulky plesiosaurs may not have been bad swimmers after all
The ancient animals’ large size may have made up for the water resistance they faced due to their body shape
Plesiosaurs once swam the world’s oceans. Fossils have revealed that some of these animals had extremely long necks — sometimes much longer than the rest of their bodies. Scientists thought the water resistance caused by such awkward features would make these creatures slow swimmers. But plesiosaurs might have been faster than realized.
Sergey Krasovskiy/Stocktrek Images/Getty Images
Share this:
- Share via email (Opens in new window) Email
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window) Pinterest
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Share to Google Classroom (Opens in new window) Google Classroom
- Click to print (Opens in new window) Print
With broad bodies and often lanky necks, plesiosaurs didn’t look like swift swimmers. But these ancient reptiles’ large size may have made up for their not-so-streamlined shapes to help them cut through water quickly.
Plesiosaurs (PLEE-see-oh-sores) prowled the seas during the Mesozoic era, tens of millions to hundreds of millions of years ago. These animals had striking shapes that greatly differed from sea creatures alive today, says Susana Gutarra Diaz. She’s now a biologist at the Natural History Museum in London, England.
Plesiosaurs swam with two pairs of paddle-like flippers. Some were the size of small dolphins. Others were as big as buses. And some had long necks — up to three times as long as the animal’s torso. Given these animals’ awkward physique, Gutarra Diaz and her colleagues wondered how they got around underwater.
Based on fossils, the researchers made computer models of plesiosaurs. They also modeled ichthyosaurs (IK-thee-oh-sores) for comparison. Those Mesozoic-era reptiles had much more streamlined bodies than plesiosaurs. They were built like fish and dolphins, modern animals that zoom through the water. Gutarra Diaz’s team also compared their models of extinct swimmers to those of modern cetaceans. These sea creatures include orcas, dolphins and humpback whales.
Using a computer program, the researchers watched how water flowed around the modeled animals’ bodies. This revealed how much drag each animal’s body experienced. Drag is resistance to a swimmer’s motion caused by the water.
First, the researchers set all of their virtual animals to the same size. This let the team see how each species’ shape alone impacted its drag. “If you have a very blobby shape, you create a lot of resistance,” Gutarra Diaz says. A more sleek, tapered shape reduces resistance.
But in real life, size also impacts how animals swim and the energy their motion requires. The drag of a goldfish would be drastically different than that of a blue whale because of the differences in volume and mass. So, to estimate each animal’s true swimming efficiency, the researchers watched how water flows around animals at their actual sizes. Then, they divided the total drag force for each animal by its body volume.
With size in the picture, plesiosaurs’ swimming prospects look much better. Plesiosaurs’ drag per unit volume wasn’t far from some of today’s master swimmers. The researchers shared this finding April 28 in Communications Biology.
“They’re likely not as slow as they were believed to be,” says Gutarra Diaz. She did this work while at the University of Bristol in England.
Big size comes with other benefits, too. Being big can make an animal more efficient at finding food. But get too big and it can be tough to find enough food to stay alive. As animals evolved, they had to balance both shape and size, Gutarra Diaz says. Plesiosaurs seem to have kept this balance, allowing them to swim pretty well.
What a drag
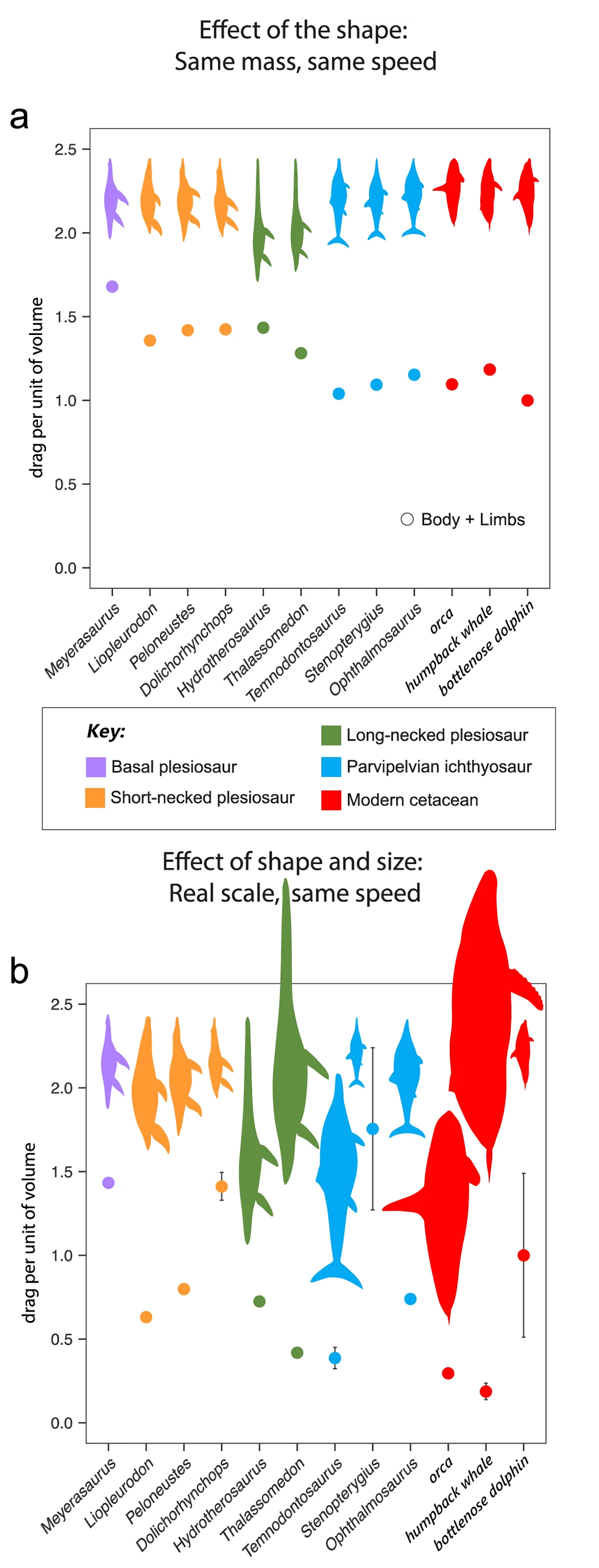
Using a computer program, researchers compared how water flows around the bodies of different animals, creating drag. These graphs show that drag force, which resists motion, for each virtual animal. Figure A shows the drag per unit volume when the animals are all assumed to be the same size. Figure B shows the drag per unit volume when the animals are their actual sizes.

Data Dive:
- Look at Figure A. Since all of these animals have the same size, the drag they experience depends only on their body shape. Which animal has the most drag per unit of volume? Which animal has the lowest drag?
- What is the range of drag for plesiosaurs in Figure A? What is the range of drag for ichthyosaurs? How do those values compare with cetaceans?
- Look at Figure B. These data show the drag experienced by animals at their real sizes. Which animal has the highest drag? Which has the lowest?
- How do the plesiosaurs compare with the ichthyosaurs in Figure B? How do the plesiosaurs compare with the cetaceans?
- Think about the shape of a jellyfish. If one were the same size as the animals in Figure A, how much drag do you think it would experience compared with the other animals? What about a shark?
- In this study, the researchers looked only at animals moving in a straight line. How might body shape impact drag when the animals turn? What are some other factors that might affect how animals swim?






