alien: (in astronomy) Life on or from a distant world.
astronomer: A scientist who works in the field of research that deals with celestial objects, space and the physical universe.
core: Something — usually round-shaped — in the center of an object.
cosmos: (adj. cosmic) A term that refers to the universe and everything within it.
force: Some outside influence that can change the motion of an object, hold objects close to one another, or produce motion or stress in a stationary object.
fundamental: Something that is basic or serves as the foundation for another thing or idea.
gravity: The force that attracts anything with mass, or bulk, toward any other thing with mass. The more mass that something has, the greater its gravity.
mass: A number that shows how much an object resists speeding up and slowing down — basically a measure of how much matter that object is made from.
neutron star: The very dense corpse of what had once been a massive star. As the star died in a supernova explosion, its outer layers shot out into space. Its core then collapsed under its intense gravity, causing protons and electrons in its atoms to fuse into neutrons (hence the star’s name). A single teaspoonful of a neutron star, on Earth, would weigh more than a billion tons.
physics: The scientific study of the nature and properties of matter and energy. Classical physics is an explanation of the nature and properties of matter and energy that relies on descriptions such as Newton’s laws of motion. Quantum physics, a field of study that emerged later, is a more accurate way of explaining the motions and behavior of matter. A scientist who works in such areas is known as a physicist.
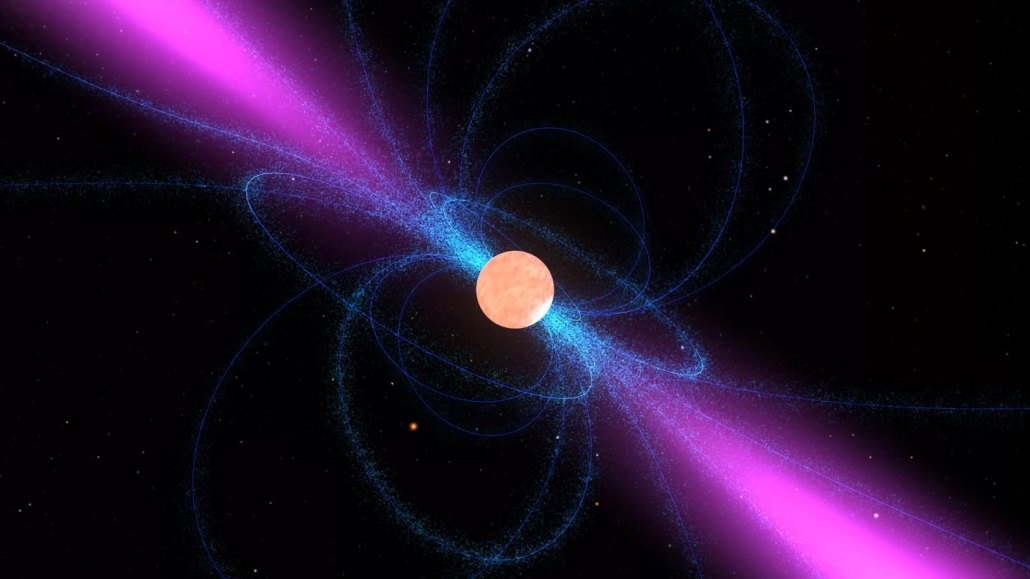
pulsar: The name for a spinning, ultra-dense neutron star. A single teaspoonful, on Earth, would weigh a billion tons. It represents the end of life for stars that had started out having four to eight times the mass of our sun. As the star died in a supernova explosion, its outer layers shot out into space. Its core then collapsed under its intense gravity, causing protons and electrons in the atoms that had made it up to fuse into neutrons (hence the star’s name). When these stars rotate, they emit short, regular pulses of radio waves or X-rays (and occasionally both at alternate intervals).
radio waves: Waves in a part of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are a type that people now use for long-distance communication. Longer than the waves of visible light, radio waves are used to transmit radio and television signals. They also are used in radar.
star: The basic building block from which galaxies are made. Stars develop when gravity compacts clouds of gas. When they become hot enough, stars will emit light and sometimes other forms of electromagnetic radiation. The sun is our closest star.
sun: The star at the center of Earth’s solar system. It is about 27,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Also a term for any sunlike star.
supernova: (plural: supernovae or supernovas) A star that suddenly increases greatly in brightness because of a catastrophic explosion that ejects most (or sometimes all) of its mass.
universe: The entire cosmos: All things that exist throughout space and time. It has been expanding since its formation during an event known as the Big Bang, some 13.8 billion years ago (give or take a few hundred million years).
wave: A disturbance or variation that travels through space and matter in a regular, oscillating fashion.