antimatter: Molecules formed by atoms consisting of antiprotons, antineutrons, and positrons.
blazar: A bright and distant active galaxy that shoots powerful jets of radiation from its center and directly toward Earth.
electric charge: The physical property responsible for electric force; it can be negative or positive.
mass: A number that shows how much an object resists speeding up and slowing down — basically a measure of how much matter that object is made from.
matter: Something that occupies space and has mass. Anything on Earth with matter will have a property described as "weight."
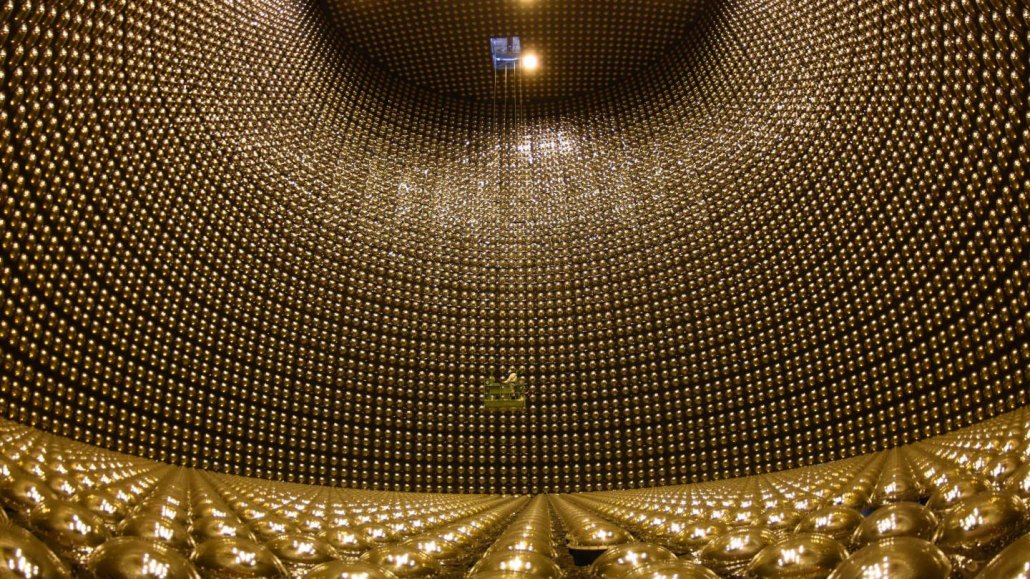
neutrino: A subatomic particle with a mass close to zero. Neutrinos rarely react with normal matter. Three kinds of neutrinos are known.
Nobel prize: A prestigious award named after Alfred Nobel. Best known as the inventor of dynamite, Nobel was a wealthy man when he died on December 10, 1896. In his will, Nobel left much of his fortune to create prizes to those who have done their best for humanity in the fields of physics, chemistry, physiology or medicine, literature and peace. Winners receive a medal and large cash award.
particle: A minute amount of something.
phenomena: Events or developments that are surprising or unusual.
physics: The scientific study of the nature and properties of matter and energy. Classical physics is an explanation of the nature and properties of matter and energy that relies on descriptions such as Newton’s laws of motion. Quantum physics, a field of study that emerged later, is a more accurate way of explaining the motions and behavior of matter. A scientist who works in such areas is known as a physicist.
sensor: A device that picks up information on physical or chemical conditions — such as temperature, barometric pressure, salinity, humidity, pH, light intensity or radiation — and stores or broadcasts that information. Scientists and engineers often rely on sensors to inform them of conditions that may change over time or that exist far from where a researcher can measure them directly.
stellar: An adjective that means of or relating to stars.
trillion: A number representing a million million — or 1,000,000,000,000 — of something.
universe: The entire cosmos: All things that exist throughout space and time. It has been expanding since its formation during an event known as the Big Bang, some 13.8 billion years ago (give or take a few hundred million years).