Genetics
-
 Genetics
GeneticsOne day, your sunscreen may be made from DNA
A new approach to sunscreen could use a thin layer of DNA to protect skin cells — and hopefully prevent cancer.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenes may predict how well the flu vaccine will work in young people
The activity of nine genes predicted how well people 35 and under would respond to the flu vaccine.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsMolecular scissors fix disease-causing flaw in human embryos
Researchers moved closer to being able to fix gene-edited embryos in people. They removed a flawed gene that causes heart failure
-
 Genetics
GeneticsScientists hide a real movie within a germ’s DNA
A gene-editing technology called CRISPR helped scientists encode a short movie in the DNA of E. coli bacteria.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsExplainer: How CRISPR works
Scientists are using a tool called CRISPR to edit DNA in all types of cells.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDNA tells tale of how cats conquered the world
Ancient DNA study suggests that domesticated cats spread across the ancient world in two waves.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDNA from African mummies tie these folk to Middle Easterners
Ancient DNA extracted from 90 Egyptian mummies reveals genetic links to Greece and the Middle East.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCool Jobs: New tools to solve crimes
Future investigators may identify criminals by the microbes they leave behind or by using DNA-like evidence from strands of their hair.
-
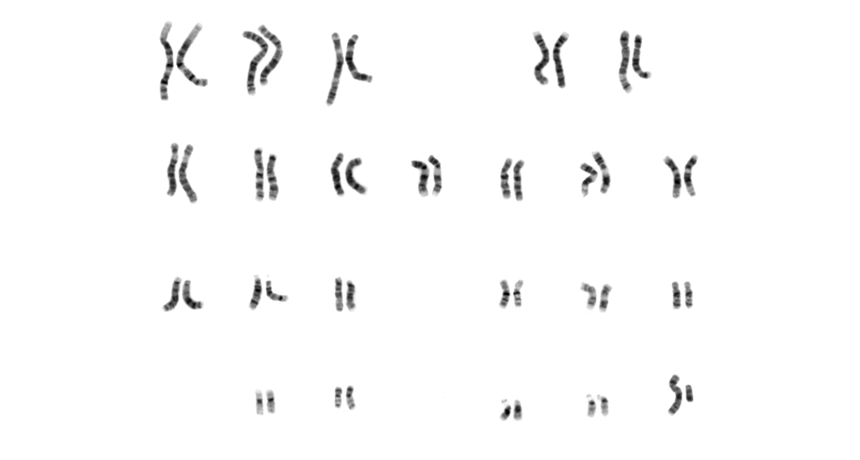 Genetics
GeneticsScientists Say: Chromosome
This threadlike structure is made of DNA wrapped around protein. It allows the 3 billion base pairs in human DNA to stay neatly packaged in a cell.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsCities drive animals and plants to evolve
Biologists are finding that some species have used genetic changes to evolve — adapt — to the pollution and other stressors that they encounter in cities.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow to view tiny parts of DNA? Make them ‘blink’
A new technique can image nanoscale structures in cells without hurting them. No dyes needed. All you have to do is stimulate them with the right color of light.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow to make a ‘three-parent’ baby
Scientists combined an egg, sperm and some donor DNA: The end result: what appears to be healthy babies.