Planets
-
 Planets
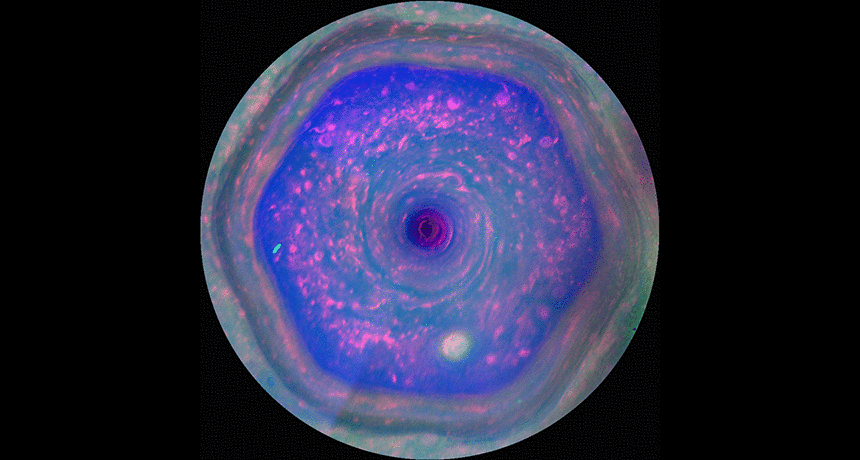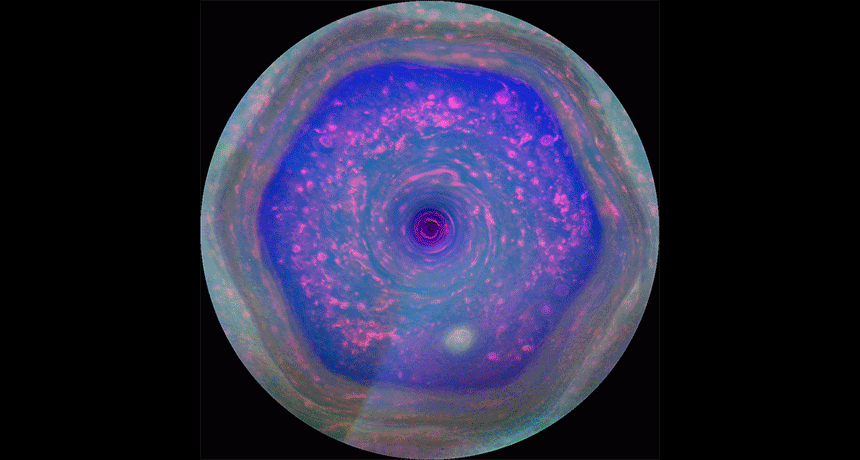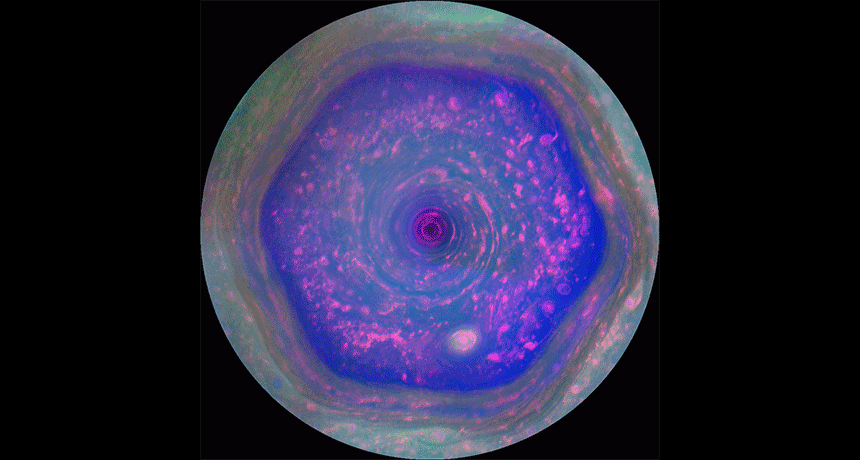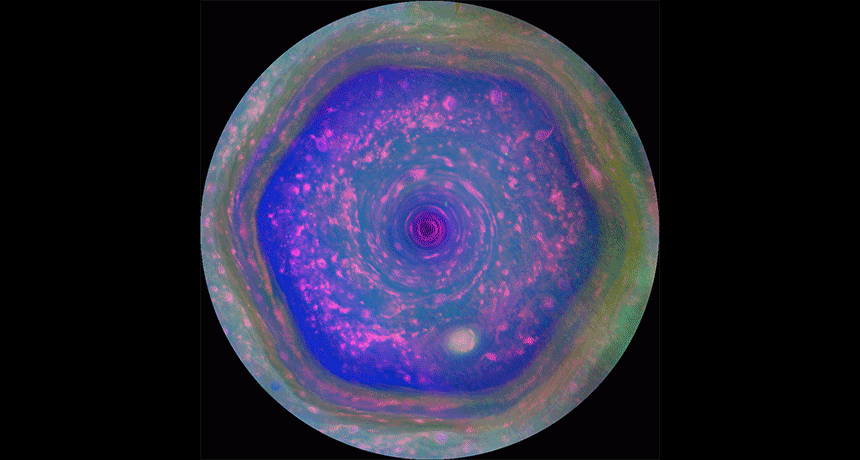
PlanetsCassini spacecraft takes its final bow
Twenty years after it left Earth, NASA’s Cassini mission is about to end — with a crash into Saturn.
-
 Earth
EarthEarly Earth may have been a hot doughnut
Synestia is the name some scientists are giving to the smooshed shape Earth might have developed after undergoing a violent cosmic smashup early in its infancy.
-
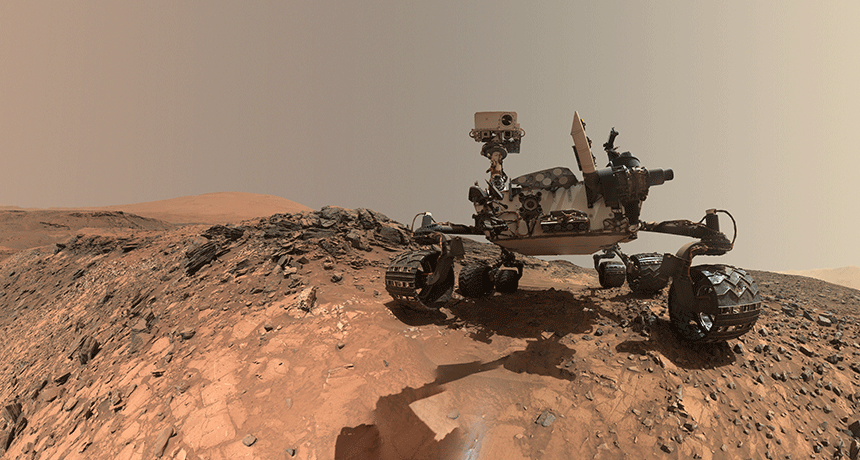 Planets
PlanetsWhat the Curiosity rover has learned about Mars so far
Scientists take stock of what the Curiosity rover has learned after five years on Mars — and what else it may turn up in the next year or so.
-
 Physics
PhysicsEarly solar system may have slung giant mud balls
The first asteroids may have been great balls of mud. That could solve some puzzling traits of meteorites.
-
 Planets
PlanetsSmall, distant worlds are either big Earths or little Neptunes
The Kepler space telescope data are in. They split Earth-like exoplanets into two groups and reveal 10 new rocky planets in the ‘Goldilocks’ zone.
-
 Planets
PlanetsJupiter may be the solar system’s oldest planet
Jupiter’s early existence may explain the odd arrangement of planets in the solar system, a new study suggests.
-
 Planets
PlanetsHot, hot planet sets sizzling new record
Astronomers have discovered an odd new exoplanet. Called KELT 9b, is the hottest non-star known.
-
 Planets
PlanetsJupiter gets surprisingly complex new portrait
NASA’s Juno spacecraft has sent back unexpected details about Jupiter, giving scientists their first close-up of this gas giant.
-
 Planets
PlanetsScientists Say: Eclipse
How the sun, moon and Earth line up determines whether there’s a solar or lunar eclipse.
-
 Earth
EarthHow Earth got its moon
How did our moon form? Scientists are still debating the answer. It may be the result of some one big impact with Earth — or perhaps many small ones.
-
 Math
MathAnalyze This: The masses of planets
Scientists discovered a solar system with planets that are similar in size and mass to Earth. Using data, we take a closer look at that similarity.
-
 Planets
PlanetsScientists Say: Dwarf planet
Dwarf planets are distinct from the full-size models. A little too small, they also have a lot of space stuff filling their path around the sun.