Uncategorized
-
 Animals
AnimalsMost species of beetles pee differently than other insects
Scientists uncover their unique system for balancing ions and water. The findings may hint at why beetles are the most diverse animals on Earth.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Space
SpaceThe Milky Way’s ‘yellowballs’ are clusters of baby stars
The mysterious cosmic objects — first spotted by citizen scientists — turn out to be infant stars of various masses.
-
 Earth
EarthLet’s learn about lightning
Around 100 times a second, every hour of every day, lightning strikes somewhere on Earth. It’s beautiful — and deadly.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentPond scum can release a paralyzing pollutant into the air
New study finds blooms of blue-green algae can seed the air with a poisonous pollutant.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Nicotine
Nicotine is an addictive substance found in tobacco plants. It's what makes it so difficult to quit smoking or vaping.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA common antibiotic might save some sick corals
The antibiotic amoxicillin stopped tissue death in corals for at least 11 months after treatment.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWarning: Wildfires might make you itch
Western wildfires are on the rise due to climate change and land use. Now a study adds eczema to the list of health risks that smoke might trigger.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate may have sent drift of the North Pole toward Greenland
This mid-1990s shift in the pole’s movement was driven by glacial melt. And that was triggered in part by climate change, a new study reports.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsThe secret to T. rex‘s incredible biting force is at last revealed
The force of a T. rex bite was roughly 6 metric tons. A new study points to what’s behind that mighty force.
By Sid Perkins -
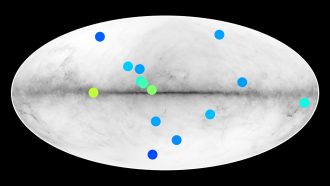 Space
SpaceStars made of antimatter could lurk in our galaxy
Fourteen sources of gamma rays in our galaxy look like they could be antistars — celestial bodies made of antimatter.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Bond
In chemistry, this attachment between atoms forms because of the power of attraction. Chemical bonds make up every solid object on Earth.
-
 Earth
EarthOnly 3 percent of Earth’s land is unchanged by people
A sweeping survey of land-based ecosystems finds that very few still support all the animals they used to. Reintroducing lost species could help.