Space
-
 Planets
PlanetsMercury’s surface may be studded with diamonds
Billions of years of meteorite impacts may have transformed much of Mercury's graphite crust into precious gemstones.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Planets
PlanetsLet’s learn about Pluto
Once known as a pipsqueak planet, Pluto is now the solar system’s best known dwarf planet.
-
 Tech
TechSpace trash could kill satellites, space stations — and astronauts
As private companies prepare to sprinkle space with tens of thousands of satellites, experts worry about the mushrooming threat of space junk.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Dark Energy
Dark energy is the unknown force causing the universe to expand faster and faster.
-
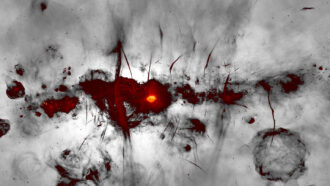 Space
SpaceWild art? No, it’s a radio image of the heart of our Milky Way
Eyelash-like radio filaments accent the brightest feature in this image — a supermassive black hole.
-
 Planets
PlanetsNo, organic molecules alone don’t point to life on Mars
These carbon-based molecules, found in a meteorite, may reflect merely a mixing of water and minerals on the Red Planet over billions of years.
By Nikk Ogasa -
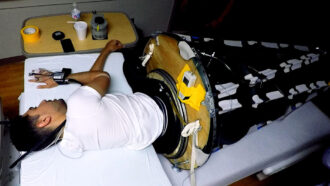 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s how a new sleeping bag could protect astronauts’ eyesight
A new sleeping bag could avoid vision problems on long space flights due to microgravity. It counters a fluid buildup behind astronauts’ eyes.
-
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: Gravity and microgravity
The force of gravity holds us on the ground, keeps planets in orbit and extends throughout space. A very weak gravitational pull is called microgravity.
By Trisha Muro and Bethany Brookshire -
 Space
SpaceExplainer: Telescopes see light — and sometimes ancient history
Different kinds of telescopes on Earth and in space help us to see all wavelengths of light. Some can even peer billions of years back in time.
By Trisha Muro -
 Space
SpaceThe long-awaited James Webb Space Telescope has a big to-do list
The James Webb Space Telescope has been in the works for so long that new fields of science have emerged for it to study.
-
 Space
SpaceScientists Say: Solar wind
This is a powerful gust of charged particles that flows out from the sun through the solar system.
-
 Space
SpaceAstronomers may have found first known planet in another galaxy
The spiral-shaped Whirlpool galaxy may be home to the first planet spotted outside our own Milky Way galaxy.