bacterial: Having to do with bacteria, single-celled organisms. These dwell nearly everywhere on Earth, from the bottom of the sea to inside animals.
bacterium: (pl. bacteria) A single-celled organism. These dwell nearly everywhere on Earth, from the bottom of the sea to inside of plants and animals.
constant: Continuous or uninterrupted. (in mathematics) A number that is known and unchanging, usually based on some mathematical definition. For example, π (pi) is a constant equal to 3.14. . . and defined as the circumference of a circle divided by its diameter.
equation: In mathematics, the statement that two quantities are equal. In geometry, equations are often used to determine the shape of a curve or surface.
exponent: A number, shown as a superscript (tiny number to the upper right of some other “base” number or mathematical expression). An exponent identifies how many times that base number or expression must be multiplied by itself.
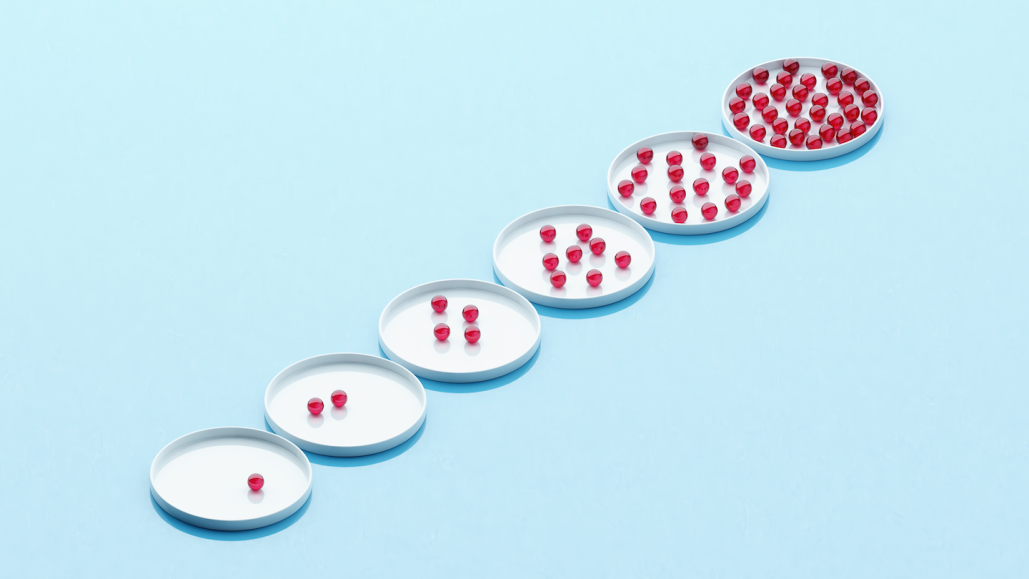
exponential: A trend or number that grows dramatically. The increase does not occur at a steady pace. Instead, it rises at an increasing rate.
petri dish: A shallow, circular dish used to grow bacteria or other microorganisms.
sun: The star at the center of Earth’s solar system. It is about 27,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way galaxy. Also a term for any sunlike star.
universe: The entire cosmos: All things that exist throughout space and time. It has been expanding since its formation during an event known as the Big Bang, some 13.8 billion years ago (give or take a few hundred million years).