Cells
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInked mice hint at how tattoos live on
Tattooed mice challenge our current understanding of how tattoos stay in humans.
By Dan Garisto -
 Life
LifeThis power source is shockingly eel-like
The electric eel’s powerful electric charge inspired this new squishy, water-based new approach to generating power.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineE-cigarettes don’t need nicotine to be toxic
E-cigarettes without nicotine can still be toxic. New studies find the flavorings in e-cigarettes can harm cells of the human immune system.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman cells form the basis of this artificial eye
Real or fake — you be the judge. Human cells were used to create this test bed for studying both the eye and eye-disease therapies.
-
 Life
LifeScientists Say: Archaea
Archaea are single-celled organisms that live anywhere from hot springs to your gut. Scientists used to think they were bacteria, but now they know they are their own domain.
-
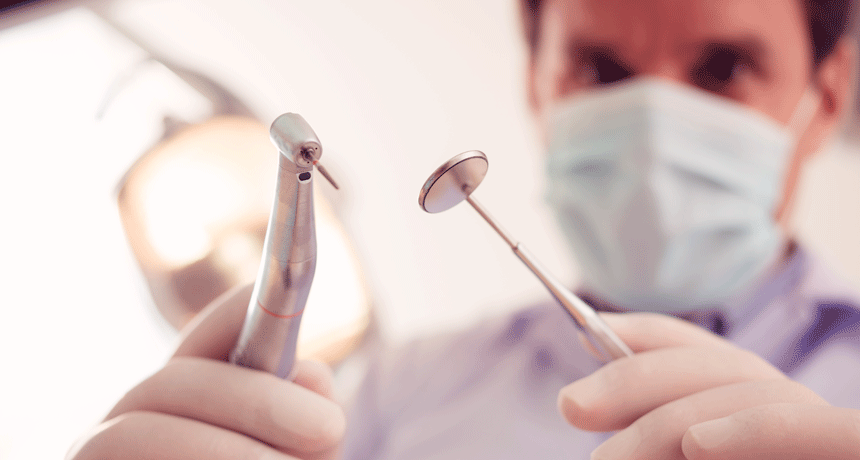 Archaeology
ArchaeologyCool Jobs: Drilling into the secrets of teeth
A bioengineer, a biologist and an archaeologist all study teeth to explore new materials, to grow better tissues and to learn more about prehistoric humans.
-
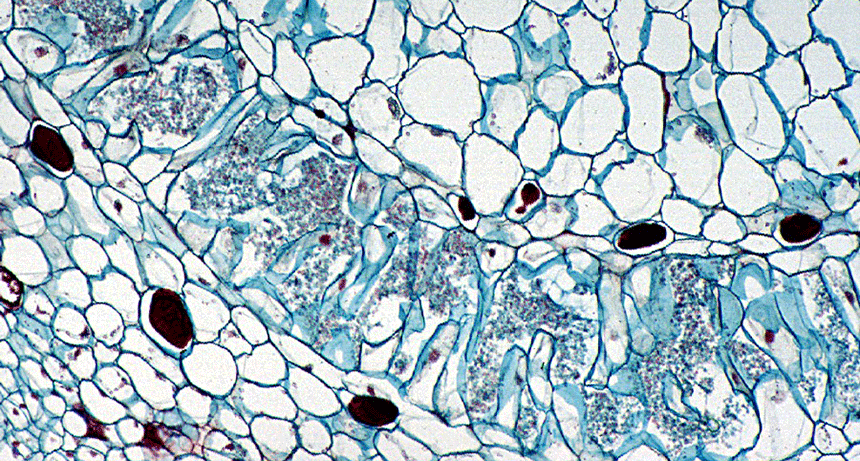 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Microbiome
You’ve got company. Every animal and plant has microscopic organisms living on and in them. These include bacteria, protists, archaea, fungi and viruses.
-
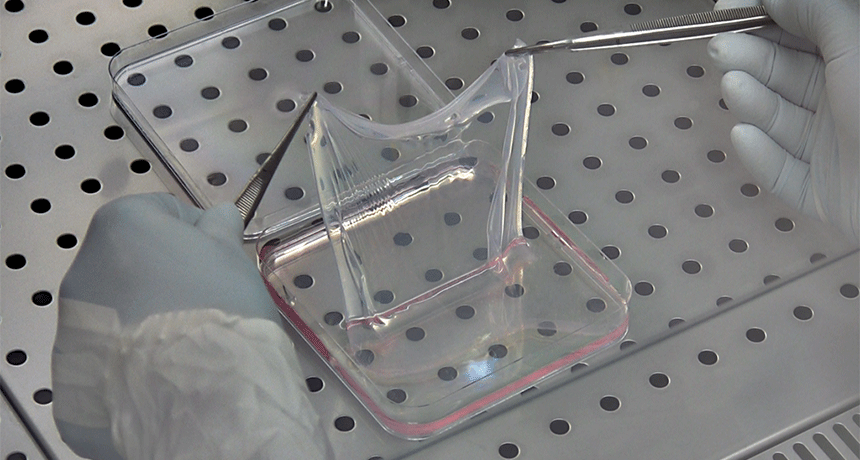 Genetics
GeneticsDoctors repair skin of boy dying from ‘butterfly’ disease
Researchers fixed a genetic defect, then replaced about 80 percent of a child’s skin. This essentially cured the boy’s life-threatening disease.
-
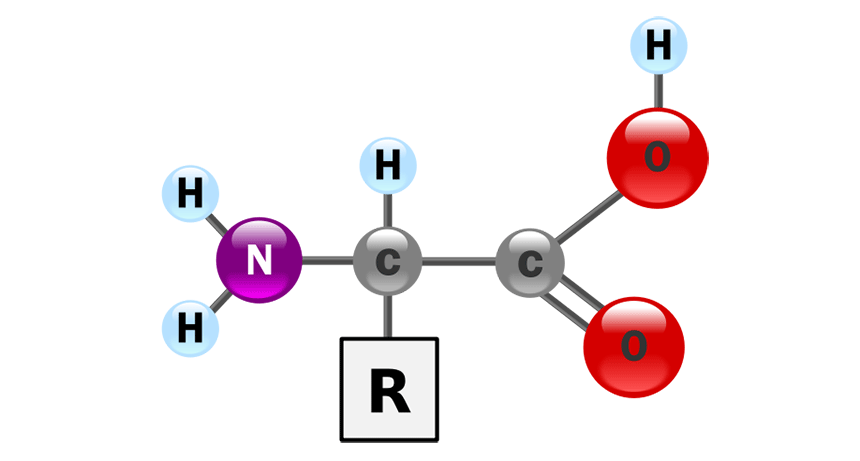 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Amino Acid
Amino acids are small molecules that make up proteins and serve as messengers in our cells.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is a hormone?
Various tissues secrete special chemicals, known as hormones. They travel, usually in blood, to a particular distant site where they tell certain cells it’s time to go to work.
By Janet Raloff -
 Chemistry
ChemistryWhen bitter + bitter = sweet
Two artificial sweeteners lose their bitter aftertastes when combined together. Scientists have just figured out why.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySuper-chilled imaging technique brings its developers the Nobel Prize in chemistry
Three men who helped develop a super-high-resolution imaging technique for proteins, viruses and more received the 2017 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
By Carolyn Gramling and Laurel Hamers