Life
-
 Health & Medicine
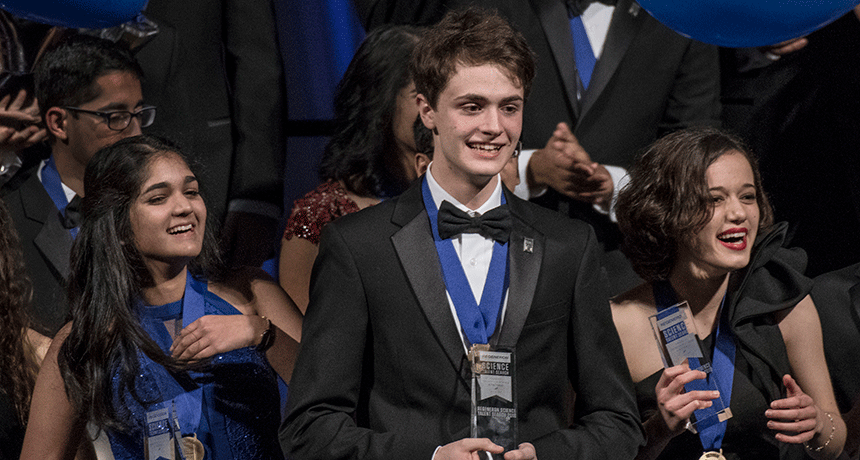
Health & MedicineTeens win big prizes for research on potato killer, vaping and a rare disease
The Regeneron Science Talent Search awarded more than $2 million in prizes this year. This year’s top winners tackled plant disease, vaping and more.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists recruit bloodsucking leeches as research assistants
By analyzing a slimy, bloodsucking leech’s last meal, scientists can identify which animals had been living near it.
By Yao-Hua Law -
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: DNA hunters
Snippets of DNA can be left behind by a passing organism. Some researchers now act as wildlife detectives to identify the sources of such cast-off DNA.
-
 Animals
AnimalsVenus flytraps tend not to eat their pollinators
A first-ever study of what pollinates a Venus flytrap finds little overlap between the critters that serve as pollinators and those that are prey.
-
 Animals
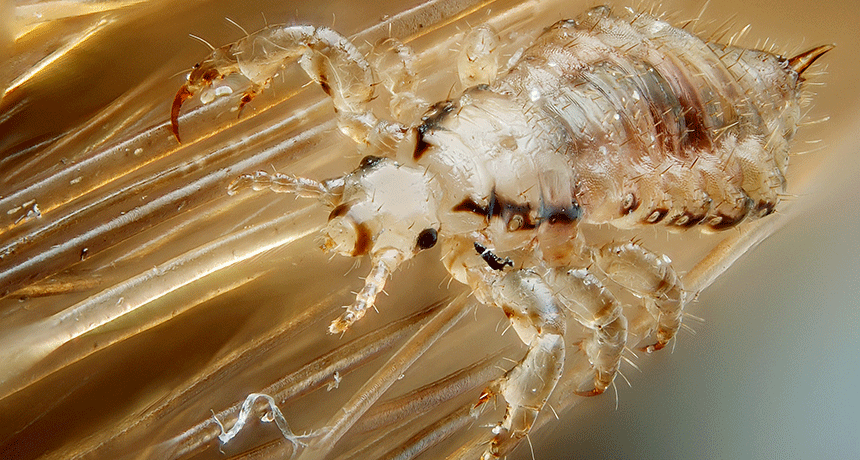
AnimalsScientists Say: Ectoparasite
Many people think of parasites as organisms that live inside their hosts. But some of them can be found on the outside instead.
-
 Fossils
FossilsAncient jaw suggests humans left Africa earlier than thought
A fossil jaw found in a cave in Israel is at least 177,000 years old. The scientists who found it think it shows humans left Africa much earlier than thought.
By Bruce Bower -
 Brain
BrainEn route to Mars, astronauts may face big health risks
Going into space brings the thrill of a new frontier — and risks that scientists are racing to understand, from radiation to isolation.
-
 Animals
AnimalsYuck! Bedbug poop leaves lingering health risks
Chemical residues left by bedbugs can persist, even when the pests have been eradicated. This may explain lingering allergic symptoms in cleaned up homes, a new study concludes.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsCan DNA editing save endangered species?
Scientists may be able to help endangered species by changing the genes of a whole population of wild animals. But some question whether that is wise.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHuman waste could power plastic-making in space
Someday recycled urine and exhaled breath could feed specially engineered yeast to make plastics and other useful chemicals on long space missions.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman cells form the basis of this artificial eye
Real or fake — you be the judge. Human cells were used to create this test bed for studying both the eye and eye-disease therapies.
-
 Life
LifeDefining a dinosaur is now far harder
New fossil finds are making it difficult to say for certain what makes dinosaurs unique.