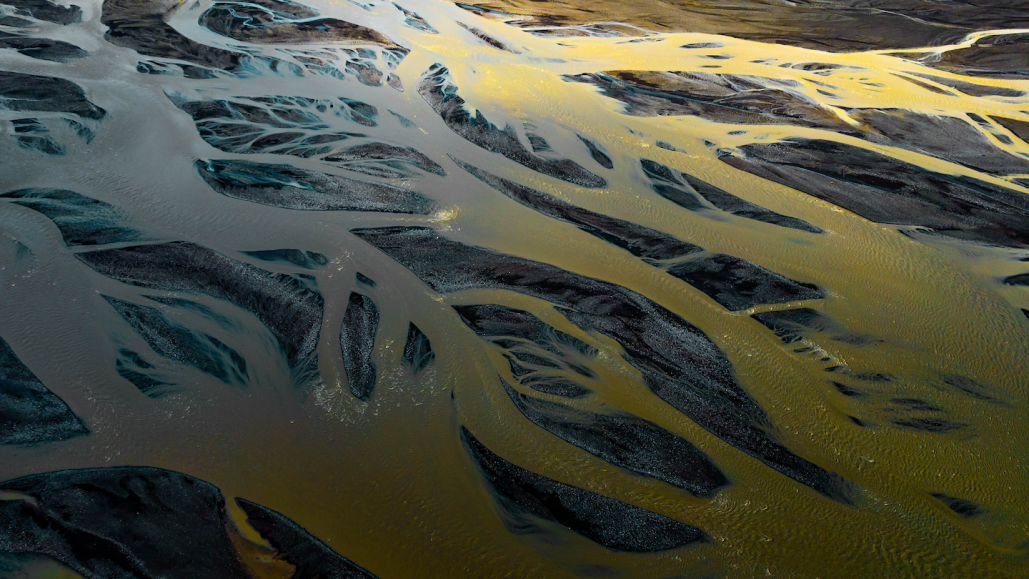
basin: (in geology) A low-lying area, often below sea level. It collects water, which then deposits fine silt and other sediment on its bottom. Because it collects these materials, it’s sometimes referred to as a catchment or a drainage basin.
climate: The weather conditions that typically exist in one area, in general, or over a long period.
climate change: Long-term, significant change in the climate of Earth. It can happen naturally or in response to human activities, including the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of forests.
downstream: Further on in the direction in which a stream is flowing or the path stream water takes as it flows towards a lake or sea.
ecosystem: A group of interacting living organisms — including microorganisms, plants and animals — and their physical environment within a particular climate. Examples include tropical reefs, rainforests, alpine meadows and polar tundra. The term can also be applied to elements that make up some artificial environment, such as a company, classroom or the internet.
freshwater: A noun or adjective that describes bodies of water with very low concentrations of salt. It’s the type of water used for drinking and making up most inland lakes, ponds, rivers and streams, as well as groundwater.
glacier: A slow-moving river of ice hundreds or thousands of meters deep. Glaciers are found in mountain valleys and also form parts of ice sheets.
meltwater: The water that comes from melting ice. The quantities can be large and show up quickly when it comes from melting glaciers, ice sheets and snow-capped mountains.
resistance: (in physics) Something that keeps a physical material (such as a block of wood, flow of water or air) from moving freely, usually because it provides friction to impede its motion.