Chemistry
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Zirconium
Zirconium is a metal that knows the meaning of tough. It’s so heat resistant that it’s used for molds to shape melted metals, and so radiation resistant that it coats nuclear reactors.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryThis rewritable paper depends on disappearing ink
Scientists have made a new rewritable paper that can hold text and images for at least six months. It also can be reused more than 100 times.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySome plastics learn to repair themselves
A new material can fix its own scratches and small cracks. One day, it also may make self-healing paints and plastics possible.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySix things that shouldn’t pollute your drinking water
These are why drinking untreated water can be harmful. But keep in mind, today’s water-treatment plants still won’t remove all of these.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExplainer: How is water cleaned up for drinking
Unless you’re drinking well water, city folks typically get drinking water that has been treated in a water-treatment plant. Here’s what that means.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySuper-water-repellent surfaces can generate energy
Scientists knew they could get power by running salt water over an electrically charged surface. But making that surface super-water-repellent boosts that energy production, new data show.
By Ilima Loomis -
 Chemistry
ChemistryDon’t flush your contact lenses
One in five people who wear contact lenses flush their used eyewear down the sink or toilet. That plastic pollutes the environment and can harm wildlife.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryThree take home chemistry Nobel for harnessing protein ‘evolution’
New ways to create customized proteins for use in biofuels and medicines earned three researchers the 2018 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
By Maria Temming and Laurel Hamers -
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Kelvin
Kelvin is a temperature scale. It’s based around the concept of “absolute zero,” a temperature so cold that molecules stop moving.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists find an easier way to trap carbon dioxide in rock
Scientists have found a much faster and easier way to trap CO2 in minerals. If they can scale it up, it might one day help to slow climate change.
-
 Earth
EarthExplainer: CO2 and other greenhouse gases
Carbon dioxide is just one of several chemicals that contribute to the greenhouse effect. Nitrous oxide, methane and CFCs are other big contributors.
-
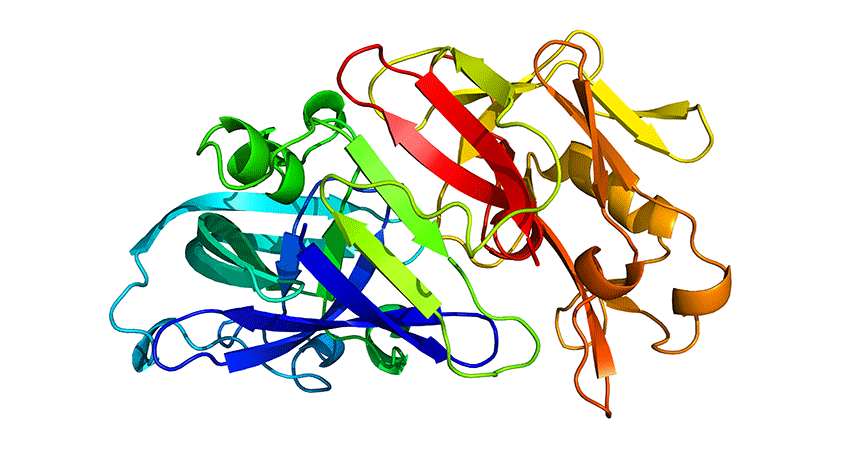 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Peptide
Peptides are short chains made of smaller molecules called amino acids. These chains can form proteins, and they can also do work on their own.