Life
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists Say: Nematocyst
Nematocysts are special cells in some ocean critters, such as jellyfish, sea anenomes and corals. They have a barb coated in venom that shoots out at their prey.
-
 Animals
AnimalsKoala genes could help scientists save these furry animals
Scientists have examined the clues within koalas’ genetic instruction book. They are learning more about how to save these cuddly creatures.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThere’s more than one way to build a giant dinosaur
Some early long-necked dinosaurs may have built big bodies from a different blueprint than their later giant relatives.
-
 Brain
BrainTaste good? Senses inform the brain — but don’t tell everyone the same thing
Whether something tastes appetizing depends on what a host of different sensory nerves collectively tell the brain. Warning: Sometimes they aren’t dependable — or even truthful.
By Lela Nargi -
 Brain
BrainExplainer: Taste and flavor are not the same
What’s behind a food’s flavor? More than what we taste, it turns out.
By Lela Nargi -
 Life
LifeBird poop helps keep coral reefs healthy, but rats are interfering
Eradicating invasive rats from islands may help boost numbers of seabirds. The birds’ droppings provide nutrients to nearby coral reefs.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesFinding living Martians just got a bit more believable
What might a real Martian look like? Scientists have a better idea after identifying a buried liquid lake on the Red Planet.
-
 Animals
AnimalsElectric currents in the air may cue ‘ballooning’ spiders on when to take off
Some spider species float on the breeze using a parachute of silk. A new study suggests electrical charges in the air help spiders time these flights.
-
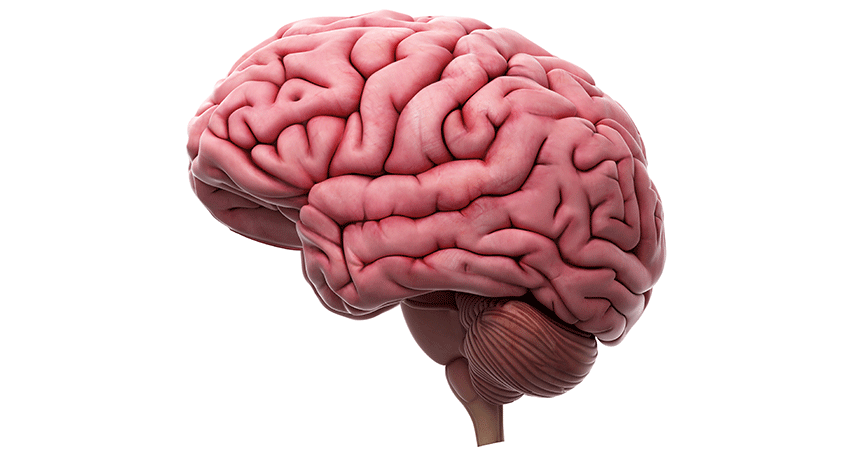 Brain
BrainScientists Say: Ventral striatum
The ventral striatum is an area of the brain that plays an important role in mood, learning and addiction. It has a lot of dopamine, a chemical messenger.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s how a clam can hide within a rock
Old boring clam research has been upended after 82 years.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsToxic toads pose threat to Madagascar’s predators
The Asian common toad, an invasive species in Madagascar, produces a chemical in its skin that’s probably toxic to most of the island’s predators.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAn Asian, self-cloning tick threatens U.S. livestock
The longhorned tick spreads human diseases in its East Asian homeland. Now it’s invaded the United States. There, it has threatened mostly livestock — so far, anyway.